Ethereum is one of the most promising cryptocurrencies, but if you’re a new crypto trader, you may have also stumbled on its namesake, Ethereum Classic. Despite the name, there is actually a big difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic. For a long time, Ethereum Classic has been known as the “dark horse”. If you would like to know more about this exciting crypto, read on!
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
Ethereum Classic is a cryptocurrency and a blockchain technology, born out of the original Ethereum code. Ethereum Classic was created in 2016, after a disagreement within the original Ethereum team. The disagreement led to Ethereum splitting in two, and today you can get both Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC). The latter is characterised by a small, but dedicated development team that highlights Ethereum Classic’s decentralised nature, its handling of “smart contracts”, and the possibility of sidechains.
 Where can I trade Ethereum Classic?
Where can I trade Ethereum Classic?
After its creation, Ethereum Classic (ETC) was distributed to all those who owned original Ethereum. These users began then to trade the cryptocurrency between themselves on various platforms. Today, Ethereum Classic is widely accepted across the crypto-environment and can be traded in most places.
On the eToro trading platform, you can bet whether Ethereum Classic will go down or up in price, but you don’t have access to your own coins and wallet. The advantage of trading in this way is the fact that you don’t have to worry about various risks, such as losing all your money due to a hack. At the same time, eToro is a regulated trading platform under European regulation. This means that you shouldn’t have a problem with transferring money from eToro to your local bank. If you want to own coins, you can try Binance. However, you should know that this platform is NOT regulated.
Ethereum Classic’s background
Ethereum Classic was created in 2016, due to a disagreement within the Ethereum community. The disagreement ended with a so-called hard fork, that is a split of the existing cryptocurrency into two new chains. After the fork, both chains function as independent cryptocurrencies.
The majority of the environment retained the name Ethereum (ETH), and the minority took the name Ethereum Classic. Thus, there are now two different cryptocurrencies that run on their own blockchain. The dispute occurred after Ethereum had been exposed to a hack, and there were different ideas on how to react to it.
The great Ethereum theft and the story of the DAO
The people behind Ethereum created a fund in 2016. Its goal was to support new startups that would be based on the Ethereum blockchain. The fund was called DAO (Decentralised Autonomous Organisation), and Ethereum investors could participate in it by purchasing DAO coins, therefore obtaining decision power regarding which projects should be supported.
All of this was handled via Ethereum’s “smart contracts”, and the fund quickly got immensely popular. So much DAO was bought that in the end there was a pool of around 150 million dollars, equivalent to around 14% of Ethereum at the time.
The pool was supposed to support new startups on the Ethereum Blockchain, and all those who owned DAO coins could vote for or against various businesses suggested by the Ethereum Foundation (a powerful group behind Ethereum).
However, before long, an error was discovered in the way the pool was built, and this mistake opened a backdoor for a hack. Those that discovered the mistake released a report about the problem, with hopes that the error could be corrected.
Unfortunately, the developers were too slow to do anything about the problem, and the hackers made it away with one-third of the pool, equivalent to 50 million dollars – solely by exploiting the error described in the report.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
The case spawned a lot of frustration within the Ethereum environment. Not only huge sums of money were lost, but Ethereum’s image took a big hit as well. Many prominent people supported the new fund, and now realised that the Ethereum team apparently did not have control over their code.
Something had to be done. The majority of people behind Ethereum proposed a hard fork solution, which would isolate the stolen holdings so that hackers could not use the money. The group ended up choosing this solution, and the result became what is today known as Ethereum (ETH).
However, the smaller part of the community was dissatisfied with this solution. They did not wish for the original code to be destroyed. Moreover, the group believed that the hard fork solution was only an attempt to save those, who have supported the project (e.g. the Ethereum Foundation). In the end, the group chose not to take part in the new development, but instead continue running on the old Ethereum blockchain – today known as Ethereum Classic (ETC).
Ethereum Classic’s development after forking with Ethereum (ETH)
After the disagreement and the subsequent creation of Ethereum Classic, many of its communications are related to why Ethereum Classic is believed to be better than Ethereum. It is claimed that:
- ETC is a less decentralised version of Ethereum
- ETC is the version of Ethereum that is closest to the original code
- ETC highlights the code, and has the least human interference in it; “code is law”
Today, Ethereum Classic is its own blockchain platform and cryptocurrency and has nothing to do with Ethereum anymore. Both coins still share many of the old, original Ethereum properties, such as running smart contracts (self-executing contracts that can be created between two parties without a middleman). But since the split, both have undergone completely different updates.
Ethereum Classic has followed its own path since its creation. Today, it also has its own wallets (digital wallets that store cryptocurrencies), its own miners (helpers that run the system by keeping track of who owns what and which transfers are being done), as well as its own vision for the future.
The team behind Ethereum Classic
Since decentralisation is a kind of Ethereum Classic’s calling card, the team has decided to be relatively anonymous.
The team consists of a long list of smart and experienced developers that are actually skilled enough to keep Ethereum Classic running and develop it in a new direction at the same time.
The names of the developers will not ring any bells to most ears, but they are solid developers with sizable experience in blockchains.
If you’d like a closer look at the team behind Ethereum Classic, you can do it here:
https://www.etcdevteam.com
A modest team can mean that Ethereum Classic’s value is not inflated, which can happen in the crypto world when big names are involved.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
What makes Ethereum Classic (ETC) different from Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum (ETH) is currently slightly more popular than Ethereum Classic (ETC). This is partly due to the fact that Ethereum is better marketed, and that the founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, together with many other prominent names, chose to go with a hard fork solution described earlier.
Additionally, Ethereum (ETH) has a better homepage compared to Ethereum Classic. You can actually go to Ethereum’s homepage, and relatively quickly and easily create a new cryptocurrency
However, since Ethereum’s (ETH) network became so popular it is easily overburdened, and therefore the transfer fees are rising. This can lead to a situation where developers and traders start to switch to Ethereum Classic instead, simply because the other network is less overloaded.
Ethereum (ETH) has plans to introduce a new technology called Plasma, which can significantly improve network performance. But if it doesn’t happen soon, users may move away from Ethereum (ETH), and towards Ethereum Classic (ETC). At the beginning of March this year Ethereum Classic’s network implemented a new digital coin called Callisto that was given to every owner of ETC in a 1:1 ratio. However, it is difficult to say yet, what effects will Callisto have on the network.
Cap and miners
There are other contrasts that make Ethereum Classic differ significantly from Ethereum (ETH). There is a different cap, and miners are rewarded differently.
Ethereum Classic has decided that miners can still “mine coins” as a reward for their work – also called PoW (Proof of work). The team has chosen that the last coin will come in 2025 when the worldwide supply reaches 210 million.
In comparison, Ethereum (ETH) has no cap, i.e. nobody knows how many coins will be created. Which leads to a significant risk of inflation.
In Ethereum’s (ETH) defence, the team behind the currency plans to make it harder for miners to get rewards for creating new coins in the future (thanks to a technique called a dirty bomb). The team will instead make it easier to get rewards simply for storing coins.
This is an attempt to make miners switch from a Proof-of-work (PoW) reward system to a Proof-of-stake (PoS) one.
Besides bold, idealistic statements about decentralisation and originality, the cap differences, and the mining reward system, Ethereum Classic is also quite different from ETH on a technical level.
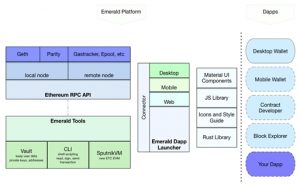 Emerald Platform
Emerald Platform
Ethereum Classic has recently launched an entirely new project called the Emerald Platform, where you can store your Ethereum Classic in an Emerald Wallet, and build new DApps (=apps on the blockchain) via Emerald Software Developer Kit (you can also build DApps on ETH, but the Emerald Platform runs only on Ethereum Classic).
Additionally, you can run a full masternode on Ethereum Classic via the Geth client, help mine (i.e. register transactions), and get paid for it in Ethereum Classic coins.
Geth was introduced by Ethereum (ETH), but Ethereum Classic developers have decided to continue running it, and have upgraded it several times. Generally speaking, a client helps run the Ethereum Classic network and performs a long list of essential functions that can be integrated into the network. In short, it’s a term relating to any node on the network able to verify the blockchain.
Sidechains
One of the most exciting differences between the two coins is the fact that Ethereum Classic has added the possibility of incorporating sidechains.
Sidechains are a new, really interesting development within the crypto/blockchain world, as they try to establish channels between individual blockchains. This means that you could for example run your Bitcoin on the Ethereum blockchain, and vice versa.
The development is quite appealing, as until now different blockchains have run on their own closed orbits. Sidechains can open the networks for each other, which may lead to a variety of possibilities and cooperation opportunities. And at this point time, Ethereum Classic and sidechains are working well.
Conclusion
Ethereum Classic still stands in the shadow of Ethereum. But thanks to several facts mentioned in this article, there may be some attractive opportunities within the environment in the long-term. The currency has a talented and hands-on team behind it and has distinguished Ethereum Classic from its competitors. The hope is that Ethereum Classic can achieve stable growth as the product will gradually improve.
The team behind Ethereum Classic is modest, and instead of bathing in the limelight, they chose to work on their product. This approach may be missing in some other cryptocurrencies, but it can also make Ethereum Classic a very good long-term investment.











